History of the Electric Guitar
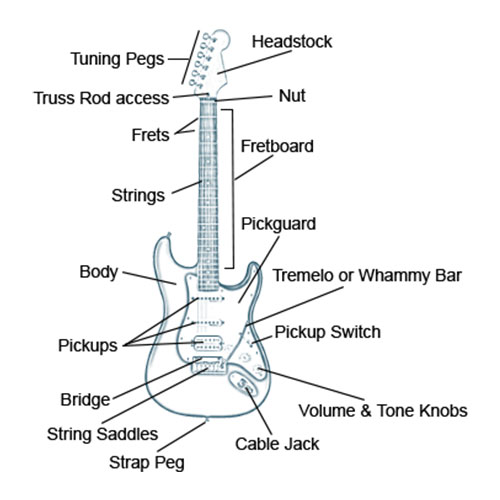
Electric Guitar Anatomy Reference
Body
The body of the guitar is hollow for acoustic guitars, and semi-hollow or solid for electric guitars. Most electric guitars are made with wood such as maple, ash, alder, mahogany as well as other types of woods. Some guitars are now made with acrylic material that allow you to see through the guitar's body.
Bridge
 The bridge holds the strings and/or saddle to the body of the guitar, and above the frets and fretboard. Guitar bridges sometimes have a tailpiece that holds the ball end of the guitar strings. From the tailpiece, the strings are placed on the saddles of the bridge (see left). It sometimes has a whammy or tremolo bar attached to the bridge. Tremolo bridges are usually found on guitars that you string the guitar through the back of the body of the guitar.
The bridge holds the strings and/or saddle to the body of the guitar, and above the frets and fretboard. Guitar bridges sometimes have a tailpiece that holds the ball end of the guitar strings. From the tailpiece, the strings are placed on the saddles of the bridge (see left). It sometimes has a whammy or tremolo bar attached to the bridge. Tremolo bridges are usually found on guitars that you string the guitar through the back of the body of the guitar.
Cable Jack
This is where you plug in an instrument cable to run through guitar effects and/or to the guitar amp.
Fretboard
The fretboard is the top side of the guitar neck containing the fret wires and usually inlays. The scale of fretboards vary on the types of guitars and their manufacturers. Fender style guitars and Gibson style guitars vary in size and typically in number of frets. Fretboards are made from a wide variety of woods including the more common maple, rosewood, or mahogany.
Frets
The frets are the metal strips or wires spaced out across the neck. Frets allow the string to resonate a note at the point where the string is pressed down on the fret. The number of frets on a guitar depends on its make and model.
Headstock
This is the head of the guitar where the tuning pegs are installed. Each guitar's headstock is differently shaped depending on its manufacturer. Some headstocks spread the tuning pegs out 3 to each side, while others have all 6 (or 7) on one side of the headstock as well as other combinations depending on manufacturer.
Nut
 The nut holds the strings above the fretboard at the top of the neck. The nut is glued to or near the headstock and top of the fretboard. Each string is placed in a notch on the nut, one for each string. This holds the strings in place and is a point of string tension. Nuts are typically made from plastic, wood, bone, ivory or other material.
The nut holds the strings above the fretboard at the top of the neck. The nut is glued to or near the headstock and top of the fretboard. Each string is placed in a notch on the nut, one for each string. This holds the strings in place and is a point of string tension. Nuts are typically made from plastic, wood, bone, ivory or other material.
Pickguard
The pickguard protects the body of the guitar and its finish from scratches from picks and fingernails. Fender Strat style guitars have pickguards that the pickups, volume and tone knobs and pickup switch are attached to. Pickguards are made out of plastic, vinyl as well as other materials.
Pickups
 Electric guitar pickups are electromagnetic, and turn the string vibrations to an electric signal. This signal is sent through the instrument cable and into the amp. Pickups are made with a magnet such as AlNiCo that is coiled with very fine copper wiring. Single coil pickups often pick up 60 cycle hum, or mains hum. Humbuckers use two pickups wound together that cancel out 60 cycle hum.
Electric guitar pickups are electromagnetic, and turn the string vibrations to an electric signal. This signal is sent through the instrument cable and into the amp. Pickups are made with a magnet such as AlNiCo that is coiled with very fine copper wiring. Single coil pickups often pick up 60 cycle hum, or mains hum. Humbuckers use two pickups wound together that cancel out 60 cycle hum.
Pickup Switch
 This switches between the guitar’s pickups. On Gibson style guitars that use two humbucker pickups, when switched all the way down, the bridge pickup is used. When switched to the middle position, both the bridge and neck pickups are used. The neck pickup is used when the switch is all the way up. Fender Strat style guitars usually have three single-coil pickups and a 5 position switch to toggle between the bridge, middle and neck pickups.
This switches between the guitar’s pickups. On Gibson style guitars that use two humbucker pickups, when switched all the way down, the bridge pickup is used. When switched to the middle position, both the bridge and neck pickups are used. The neck pickup is used when the switch is all the way up. Fender Strat style guitars usually have three single-coil pickups and a 5 position switch to toggle between the bridge, middle and neck pickups.
Saddle
 The saddle is what holds the strings up above the neck off the bridge of the guitar. On electric guitars different variations of saddles are available. Some Telecaster style guitars use 3 saddles with two strings on each. Others use individual saddles for each string. Adjusting the position of the saddles is done when intonating the guitar.
The saddle is what holds the strings up above the neck off the bridge of the guitar. On electric guitars different variations of saddles are available. Some Telecaster style guitars use 3 saddles with two strings on each. Others use individual saddles for each string. Adjusting the position of the saddles is done when intonating the guitar.
Strap Pegs
These are the pegs that hold the guitar strap to the guitar's body. These are located at the bottom of the guitar's body and somewhere around where the neck and body are connected depending on the model of guitar.
Strings
Guitar strings are made from steel, nylon, or other material such as copper, zinc and titanium. The lower strings are wound around another reinforcement string in the middle. Classical style guitars are usually strung with nylon strings.
Tone Knob
The tone knob adjusts the amount of bass or treble frequencies sent to the amp from the guitar's pickups. With this knob all the way up, you get a bright sound and a darker sound when all the way down. This also helps adjust your overall sound.
Tremolo or Whammy Bar
An arm or lever connected to the bridge. This allows the guitarist to alter the tension of the strings to create vibrato and pitch bending effects. Floyd Rose bridges lock the strings at the nut to help keep the strings in tune after the tension has been changed temporarily by the whammy bar.
Truss Rod
This adjusts the bend in the neck of the guitar. The neck is usually bowed slightly to keep strings from buzzing on frets and for the overall setup of the guitar. A single rod goes through the neck of the guitar and can be loosened or tightened to achieve this. Unless you know how to adjust this properly, it's usually a good idea to leave this as a job for luthiers or guitar techs. Improperly adjusted truss rods could potentially damage the neck of the guitar or mess up the intonation.
Tuning Pegs
 One tuning peg for each string. This is where the end of the string is wrapped typically 2 to 3 times. You tune the guitar with these pegs by twisting these to adjust string tension.
One tuning peg for each string. This is where the end of the string is wrapped typically 2 to 3 times. You tune the guitar with these pegs by twisting these to adjust string tension.
Volume Knob
The volume knob adjusts the volume of the signal sent to the guitar amp. Slight adjustments with this knob can alter the overall tone of your guitar and amp.